
Every time a nucleotide is added to the new strand only one of the four types of nucleotide has the base that can pair with the base at the position reached on the template strand.
#Sections of copied dna created on the lagging strand free
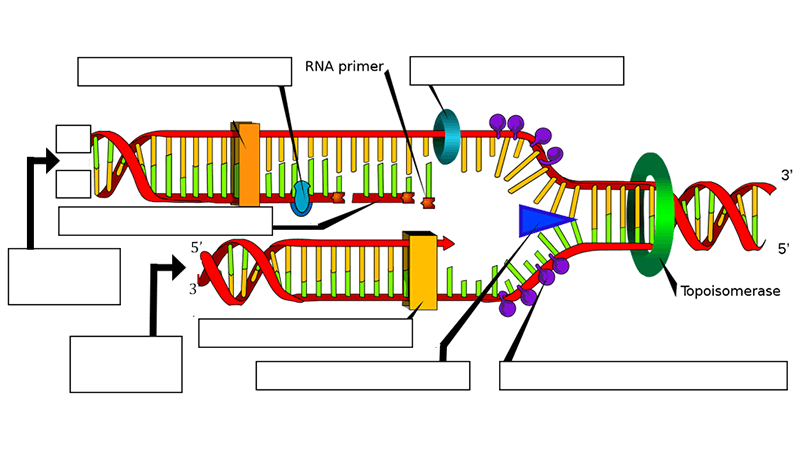
Free nucleotides with each of the four possible bases are available in the area where DNA is being replicated. DNA polymerase move along the template strand in the same direction, adding one nucleotide at a time. The creation of new strands is carried out by enzyme DNA polymerase Rule – one base always pairs with another is called complementary base pairing.This makes sure that the two DNA molecules that are created by DNA replication are identical in their base sequences to the parent molecule that was replicated. Since complementary bases form hydrogen bonds with each, stabilizing the structure, if a nucleotide with the wrong base started to be inserted, the hydrogen bond would not happen and the nucleotide would not be added to the chain The base sequence on the template strand determines the base sequence on the new strand, only a nucleotide carrying a base that is complementary to the next base on the template strand can successfully be added to the new strand.  Therefore DNA replication is referred to as being semi-conservative. The results of this process is 2 DNA molecules, both made up of the original strand and a newly synthesized strand. New strands are formed by adding nucleotides, one by one, and linking them together. The new strands are used as a guide or template for the creation of a new strand. When a cell is preparing to divide, the two strands of the double helix separate. One strand will be from the original template molecule. The last process is termination where a special DNA sequence in the template strand causes RNA polymerase to detach and transcription to terminate.DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, because when a new double-stranded DNA molecule is formed: It requires DNA polymerase to move in the opposite direction - causing the formation of short and discontinous segments - called the Okazaki fragments. For one strand called the leading strand, this only needs to happen once as it moves in the same direction as the replication fork- the direction where the helicase enzyme is unwounding the DNA. However, it only attaches new neucleotides to the free 3' hydroxyl end. The enzyme responsible for this is DNA polymerase III.
Therefore DNA replication is referred to as being semi-conservative. The results of this process is 2 DNA molecules, both made up of the original strand and a newly synthesized strand. New strands are formed by adding nucleotides, one by one, and linking them together. The new strands are used as a guide or template for the creation of a new strand. When a cell is preparing to divide, the two strands of the double helix separate. One strand will be from the original template molecule. The last process is termination where a special DNA sequence in the template strand causes RNA polymerase to detach and transcription to terminate.DNA replication is a semi-conservative process, because when a new double-stranded DNA molecule is formed: It requires DNA polymerase to move in the opposite direction - causing the formation of short and discontinous segments - called the Okazaki fragments. For one strand called the leading strand, this only needs to happen once as it moves in the same direction as the replication fork- the direction where the helicase enzyme is unwounding the DNA. However, it only attaches new neucleotides to the free 3' hydroxyl end. The enzyme responsible for this is DNA polymerase III. 
Here, two new strands of DNA are assembled using the parent DNA as a template.
Another protein then helps stabilize the newly single-stranded DNA.
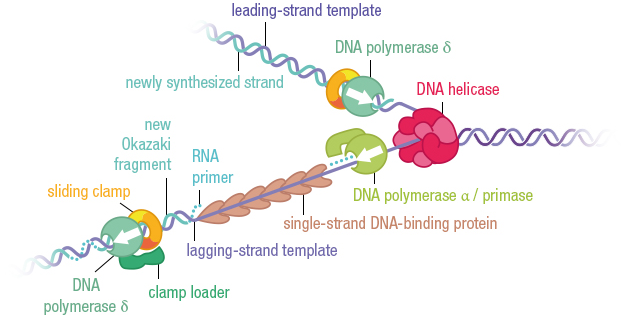
Helicase is a group of enzyme that helps unwounds DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. Here, several initiator proteins bind to the DNA and begin the process of unwinding the double helix. It begins at a specific nucleotide sequence, called the origin of replication. Hence two newly generated molecules remain similar to the parent DNA molecule.ĭNA replication occurs in three basic phases which relies on the structural features of DNA and a number of specialized enzymatic proteins. This means that each new molecule of DNA contains one strand of the parent molecule and one complementary strand that is newly synthesized (daughter strand).








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
